September 19 Peace Love Art Activism
Anarchism in the US
September 19, 1892: Andrew Berkman is sentenced to twenty-two years in prison for the attempt on steel magnate Henry Clay Frick’s life on July 23, 1892. [1970 NY Review article] (see June 1893)
September 19 Peace Love Art Activism
BLACK HISTORY
Booker T. Washington
July 4, 1881: Booker T. Washington opened the Tuskegee Normal and Industrial Institute in Tuskegee, Ala. The only building on campus was a shanty with a roof so leaky a student held an umbrella over Washington’s head while he taught. [Black Past article] (see In August)
Emmett Till
September 19, 1955: the kidnapping (only) trial of J W Milam and Roy Bryant opened in Sumner, Mississippi, the county seat of Tallahatchie County. Jury selection begins and, with blacks and white women banned from serving, an all-white, 12-man jury made up of nine farmers, two carpenters and one insurance agent was selected.
Emmett’s mother, Mamie Till Bradley, departed from Chicago’s Midway Airport to attend the trial. (see Emmett Till)
September 19 Peace Love Art Activism
Nuclear/Chemical News
Operation Plumbbob
September 19, 1957: the US detonated a 1.7 kiloton nuclear weapon in an underground tunnel at the Nevada Test Site (NTS), a 1,375 square mile research center located 65 miles north of Las Vegas. The test, known as Rainier, was the first fully contained underground detonation and produced no radioactive fallout. A modified W-25 warhead weighing 218 pounds and measuring 25.7 inches in diameter and 17.4 inches in length was used for the test. Rainier was part of a series of 29 nuclear weapons and nuclear weapons safety tests known as Operation Plumbbob that were conducted at the NTS between May 28, 1957, and October 7, 1957. (related NYT article) (see Sept 29)
Cuban Missile Crisis
September 19, 1962: the United States Intelligence Board (USIB) approved a report on the Soviet arms buildup in Cuba. Its assessment, stated that some intelligence indicates the ongoing deployment of nuclear missiles to Cuba. The Soviet Union above ground nuclear test. 1.5 – 10 megaton. (CW/NN, see Sept 25; see Cuban Missile Crisis for expanded story)
September 19 Peace Love Art Activism
The Cold War
No Disneyland for Khrushchev
September 19, 1959: Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev had arrived in the US on September 15 for a summit meeting with President Eisenhower. The Soviet leader indicated a desire to see Hollywood. September 19 began pleasantly enough, with a tour of the Twentieth Century Fox Studios. Khrushchev was taken to the sound stage for the movie “Can-Can” and was immediately surrounded by the cast of the film, including Shirley MacLaine and Juliet Prowse. The cast members performed a number from the film. Frank Sinatra was brought in to serve as an unofficial master of ceremonies later lunched with an obviously delighted Khrushchev. (see Disneyland for more)
September 19 Peace Love Art Activism
Teenage Culture
September 19 – 25, 1960: “The Twist” by 18-year-old Chubby Checker #1 Billboard Hot 100 (see January 1962). The song was written by Hank Ballard and originally the B-side of Hank Ballard & the Midnighters’ “Teardrops on Your Letter” in 1959.
Checker was born Ernest Evans. His boss nicknamed him Chubby. He made a private recording, “The Class,” on which he imitated many singers of the time including Fats Domino. The record was given to Dick Clark whose wife, after Ernest Evans said his nickname was Chubby, asked, “As in Checker?” referring to Fats Domino. The name stuck. (see March 1963)
September 19 Peace Love Art Activism
Vietnam
September 19, 1969: President Nixon announced the cancellation of the draft calls for November and December. He reduced the draft call by 50,000 (32,000 in November and 18,000 in December). This move accompanied his twin program of turning the war over to the South Vietnamese concurrent with U.S. troop withdrawals and was calculated to quell antiwar protests by students returning to college campuses after the summer. (see Sept 23)
September 19 Peace Love Art Activism
US Labor History
September 19, 1973: a judge sentenced Aubran W Martin, one of the three gunmen convicted in the 1969 Yablonski family murders, to die in the electric chair. [Pittsburgh Post Gazette story on murders] (Yablonski, see April 8, 1974; Labor, see Nov 12)
September 19 Peace Love Art Activism
INDEPENDENCE DAY
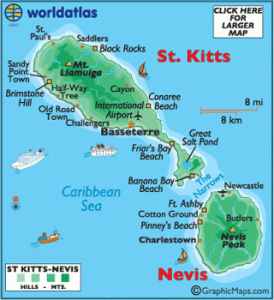
September 19, 1983: Saint Kitts and Nevis independent of the United Kingdom. [NYT article] (see January 1, 1984)
September 19 Peace Love Art Activism
Sexual Abuse of Children
September 19, 2002: the Boston Archdiocese reached a $10m settlement with victims of John Geoghan, retracting a previous settlement of $30m which the Church said would have bankrupted the archdiocese. (NYT article) (see Oct 7)
September 19 Peace Love Art Activism
Hurricane Katrina
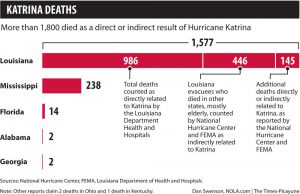
September 19, 2005: Louisiana’s official death toll stood at 973. (see Katrina for expanded story)
September 19 Peace Love Art Activism
LGBTQ
Don’t ask, don’t tell
September 19, 2011: the US military’s “Don’t ask, don’t tell” policy officially ended. [Washington Post article] (see September 20, 2011)
Don’t Ask Don’t Tell/Year 1
September 19, 2012: the one-year anniversary of the end of the “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell” policy passed with little notice because the policy had been so quickly implemented with so little disruption. Gay, lesbian and bisexual service members were thought to make up at least 2 percent of the military’s 2.2 million forces on active duty, in the reserves, and the National Guard. (see October 18, 2012)
September 19 Peace Love Art Activism
FREE SPEECH & Colin Kaepernick
September 19, 2016: four Philadelphia Eagles raised their fists during the anthem
Prior to the game, Malcolm Jenkins said the Eagles would protest during the anthem. Jenkins was joined by Steven Means, Ron Brooks and Marcus Smith in raising a fist while standing during the anthem. [Washington Post article] FS & CK, see Sept 20)