July 20 Peace Love Art Activism
Native Americans
July 20, 1881: five years after General George A. Custer’s infamous defeat at the Battle of Little Bighorn, Hunkpapa Teton Sioux leader Sitting Bull surrendered to the U.S. Army, which promised amnesty for him and his followers. Sitting Bull had been a major leader in the 1876 Sioux uprising that resulted in the death of Custer and 264 of his men at Little Bighorn. Pursued by the U.S. Army after the Indian victory, he escaped to Canada with his followers. Sitting Bull was assigned to the Standing Rock reservation in South Dakota in 1883. Seven years later he was dead, killed by Indian police when he resisted their attempt to arrest him for his supposed participation in the Ghost Dance uprising. (next NA, see October 26, 1882; Sitting Bull, see December 15, 1890)
July 20 Peace Love Art Activism
US Labor History
July 20, 1899: New York City newsboys, many so poor that they were sleeping in the streets, begin a 2-week strike. Several rallies drew more than 5,000 newsboys, complete with charismatic speeches by strike leader Kid Blink, who was blind in one eye. The boys had to pay publishers up front for the newspapers; they were successful in forcing the publishers to buy back unsold papers. [2017 NY Daily News story] (see Sept 30)
July 20 Peace Love Art Activism
BLACK HISTORY
UNIA
July 20, 1914: Marcus Garvey and Amy Ashwood founded the Universal Negro Improvement Association and African Communities League. The U.N.I.A. was originally conceived as a benevolent or fraternal reform association dedicated to racial uplift and the establishment of educational and industrial opportunities for blacks. (Nat’l Humanities Center article) (BH, see February 8, 1915; see Garvey for expanded story)
Jack Johnson
July 20, 1920: self-exiled boxer Jack Johnson returned to the U.S. He surrendered to federal agents at the Mexican border and was sent to the United States Penitentiary, Leavenworth to serve his sentence in September 1920.
He was released on July 9, 1921. (BH, see Aug 1 > 31; JJ, see May 24, 2018)
Albany Movement
July 20, 1962: Robert Elliott, a Federal judge had issued an injunction against mass marches using the legal reasoning that demonstrations require the presence of policemen; policemen who are present during demonstrations could not handle other complaints of other citizens in the community; therefore, the demonstrations were denying other citizens — white citizens — equal protection of the law. Thus White citizens were denied equal protection.
Defying that injunction, 160 protesters were arrested. (see Albany Movement for expanded story)
SOUTH AFRICA/APARTHEID
July 20, 1985: P. W. Botha declared a state of emergency in 36 magisterial districts of South Africa amid growing civil unrest in black townships. (see June 12, 1986)
Trayvon Martin Shooting
July 20, 2013: one week after a Florida jury found George Zimmerman not guilty in the death of unarmed teen Trayvon Martin, rallies were scheduled in 100 cities to press for civil rights charges against the former neighborhood watch leader. (BH, see Sept 13; TMS, see August 28)
July 20 Peace Love Art Activism
Religion and Public Education
SEPARATION OF CHURCH AND STATE
July 20, 1925: with the proceedings taking place outdoors due to the heat, the defense — in a highly unusual move — calls Bryan to testify as a biblical expert. Clarence Darrow asks Bryan a series of questions about whether the Bible should be interpreted literally. As the questioning continued, Bryan accuses Darrow of making a “slur at the Bible,” while Darrow mocks Bryan for “fool ideas that no intelligent Christian on earth believes.” (see Trial for expanded story)
July 20 Peace Love Art Activism
Cold War
Military Draft
July 20, 1948: following World War II, the US moved quickly to demobilize the vast military it had constructed and by 1948, less than 550,000 men remained in the U.S. Army. This rapid decline in the size of America’s military concerned U.S. government officials, who believed that a confrontation with the Soviet Union was imminent.
On this date President Harry S. Truman instituted a military draft with a proclamation calling for nearly 10 million men to register for military service within the next two months. (Rally Point article)
FREE SPEECH
July 20, 1948: the top leaders of the Communist Party were arrested under the Smith Act. After a stormy trial, in which the prosecutor relied primarily on Marxist writings and offered no evidence of any planned effort to overthrow the U.S. government, 11 party leaders were convicted. (shmoop article) (Red Scare, see Aug 3; Free Speech, see November 1, 1948; Supreme Court decision re Smith Act, see June 4, 1951)
Cuba
July 20, 2015: in a symbolic ceremony marking the end of 54 years of hostility, Cuba raised its flag over a limestone mansion in Washington, DC and officially reopened its U.S. Embassy. Hundreds of people, including U.S. lawmakers, diplomats and others joined visiting Cuban Foreign Minister Bruno Rodríguez, who led a delegation of about 30 officials from Havana, including Cuba’s chief negotiator on the normalization of diplomatic ties, Josefina Vidal. The U.S. would wait to raise an American flag and unveil a new sign at its Havana embassy until Secretary of State John Kerry traveled there to do the honors later that summer. (Reuters article) (CW & Cuba, see Aug 14)
July 20 Peace Love Art Activism
July 20 Music et al
Surf City
July 20 – August 2, 1963, “Surf City” by Jan & Dean #1 on the Billboard Hot 100. Co-written with Brian Wilson.
Something New
July 20, 1964, The Beatles: released Something New, a US only release. (see July 25)
- Label: Capitol (US)
- Recorded: 2 9 January, 25–27 February,
1 March and 1–4 June 1964
Hugh Masekela
July 20 – August 2, 1968: “Grazing in the Grass” by Hugh Masekela #1 on the Billboard Hot 100.
Road to Bethel
 July 20, 1969, The Road to Bethel and the Woodstock Festival: someone nails sign “Stop Max’s Hippy Music Festival” to tree at driveway entrance. Angers Yasgur and convinces him his decision to allow concert on his property was the right decision. (see Chronology for expanded story )
July 20, 1969, The Road to Bethel and the Woodstock Festival: someone nails sign “Stop Max’s Hippy Music Festival” to tree at driveway entrance. Angers Yasgur and convinces him his decision to allow concert on his property was the right decision. (see Chronology for expanded story )
July 20 Peace Love Art Activism
ADA
July 20, 1968, ADA: the first International Special Olympics Summer Games, organized by Eunice Kennedy Shriver, were held at Soldier Field in Chicago. [Special Olympics site article] (see June 19, 1970)
July 20 Peace Love Art Activism
Space Race
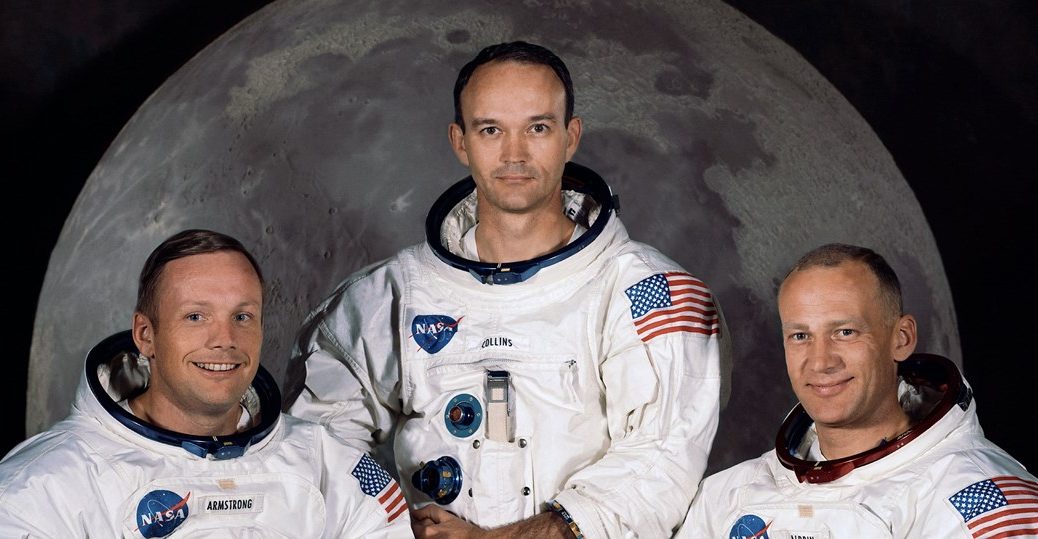
July 20, 1969: Americans Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin become the first men to walk on the moon. They then rendezvous with Michael Collins in the command module for the return to Earth. [NASA article] (see July 24)
July 20 Peace Love Art Activism
War Powers Act
July 20, 1973: the Senate approved the War Powers Act by a vote of 75 – 20. [links to NYT stories re WPA] (see Oct 4)
July 20 Peace Love Art Activism
Irish Troubles
July 20, 1982: the Provisional IRA detonated 2 bombs in central London, killing 8 soldiers, wounding 47 people. (see Troubles for expanded story)
July 20 Peace Love Art Activism
Michael Dukakis
 July 20, 1988: the Democratic National Convention in Atlanta nominated Michael Dukakis for President and Lloyd Bentsen for Vice President. [APP article]
July 20, 1988: the Democratic National Convention in Atlanta nominated Michael Dukakis for President and Lloyd Bentsen for Vice President. [APP article]
July 20 Peace Love Art Activism
Environmental Issues
July 20, 2021: wildfire smoke from the western United States and Canada stretched across the continent, covering eastern skies in a thick haze and triggering air quality alerts from Toronto to Philadelphia.
In recent weeks, a series of near-relentless heat waves and deepening drought linked to climate change had helped to fuel exploding wildfires. In southern Oregon, the Bootleg Fire grew so large and hot that it created its own weather, triggering lightning and releasing enormous amounts of smoke. But more than 80 large fires were burning across 13 American states, and many more were active across Canada.
As the smoke moved eastward across Toronto, New York and Philadelphia, concentrations of dangerous microscopic air pollution known as PM2.5 (because the particles are less than 2.5 microns in diameter) reached highs in the “unhealthy” range for most of the day. Minnesota was heavily blanketed by smoke from wildfires burning across the Canadian border, with the city of Brainerd and others recording “hazardous” levels of pollution, the highest designation of concern from the Environmental Protection Agency. [NYT article w/ video] (next EI, see July 26)
Record Heat
July 20 2023: in its monthly call, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration analyzed how June’s temperatures stacked up and said June was Earth’s hottest on record.
According to the European Union’s Copernicus Climate Change Service, the first two weeks of July were also likely the Earth’s warmest on human record, for any time of year. [NYT article] (next EI, see Aug 8)
July 20 Peace Love Art Activism
Nuclear/Chemical News
July 20, 2023: a new study, released ahead of submission to a scientific journal for peer review showed that the July 16, 1945 Trinity explosion cloud and its fallout went farther than anyone in the Manhattan Project had imagined in 1945. Using state-of-the-art modeling software and recently uncovered historical weather data, the study’s authors say that radioactive fallout from the Trinity test reached 46 states, Canada and Mexico within 10 days of detonation.
“It’s a huge finding and, at the same time, it shouldn’t surprise anyone,” said the study’s lead author, Sébastien Philippe, a researcher and scientist at Princeton University’s Program on Science and Global Security. [NYT article] (next N/C N, see Aug 8)