President Trump Wall
I will make Mexico pay…
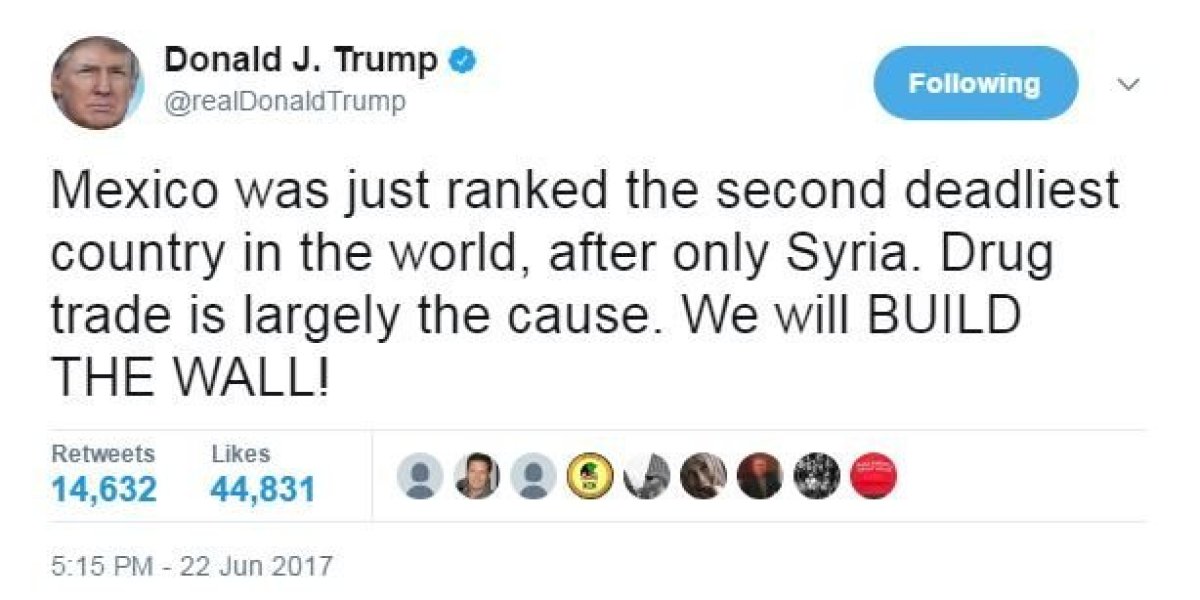
June 16, 2015: Donald Trump announced his campaign for the presidency and first mentioned his idea to build a southern border wall.
“I will build a great wall ― and nobody builds walls better than me, believe me ―and I’ll build them very inexpensively. I will build a great, great wall on our southern border, and I will make Mexico pay for that wall. Mark my words.”
Throughout his campaign, Trump regularly used a call and response with his crowds to reinforce his promise to build a wall and vilified immigrants from Mexico and Central and South America.
President Trump Wall
It’s not a fence…
August 25, 2015: Candidate Trump tweeted: Jeb Bush just talked about my border proposal to build a “fence.” It’s not a fence, Jeb, it’s a WALL, and there’s a BIG difference!
April 1, 2016: Candidate Trump tweeted: We must build a great wall between Mexico and the United States!
Aug. 31, 2016 — Candidate Trump met in Mexico City with Pena Nieto. The subject of who will pay for the border wall did not come up. At a news conference following their meeting, Pena Nieto said the bilateral relationship should be based on mutual respect.
September 1, 2016: Candidate Trump tweeted: Mexico will pay for the wall – 100%! #MakeAmericaGreatAgain #ImWithYou
November 10, 2016: two days after the election Trump adviser Rudy Giuliani stated in a CNN interview that President-elect Trump doesn’t need the support of Congress to build the wall; he can simply accomplish it through executive order. He also maintained that large portions of the wall have already been approved:
“The wall is going to take a while. Obviously he’s going to build it. It’s a campaign promise. He’s not going to break a campaign promise..he can do it by executive order by just reprogramming money within the, within the immigration service…And not only that, they have actually approved a wall for certain portions of the border that hasn’t even been built yet. So you could take a year building that out, with what has been approved.”
President Trump Wall
A fence would be OK…
November 13, 2016: Trump appeared on 60 Minutes. He said a fence would be OK, too.
STAHL (60 Minutes): You’re— you know, they are talking about a fence in the Republican Congress, would you accept a fence?
TRUMP: For certain areas I would, but certain areas, a wall is more appropriate. I’m very good at this, it’s called construction…there could be some fencing.
January 11, 2017: after repeating many times that Mexico would pay for the wall and in what would turn out to be the first of many contentious press conferences, President Trump clarified that Mexico might not be paying the upfront costs for the wall after all.
“I want to get the wall started. I don’t want to wait a year and a half until I make my deal with Mexico. They will reimburse us for the cost of the wall, whether it’s a tax or whether it’s a payment. Probably less likely that it’s a payment.”
President Trump Wall
Mexico will pay back later…
January 6, 2017: President Trump tweeted: The dishonest media does not report that any money spent on building the Great Wall (for sake of speed), will be paid back by Mexico later!
January 24, 2017: President Trump tweeted: Big day planned on NATIONAL SECURITY tomorrow. Among many other things, we will build the wall!
January 25, 2017:President Trump issued an executive order entitled “Border Security and Immigration Enforcement Improvements“. It declared:
In accordance with existing law, including the Secure Fence Act and IIRIRA, take all appropriate steps to immediately plan, design, and construct a physical wall along the southern border, using appropriate materials and technology to most effectively achieve complete operational control of the southern border;
Mexican President Enrique Pena Nieto then responded in an official address. He stated:
I am dismayed by and condemn the decision made by the United States to continue building a wall that for many years, far from uniting us, has divided us. Mexico does not believe in walls. I have said it again and again: Mexico will not pay for any wall.
January 26, 2017: Mexico’s president, Enrique Peña Nieto, cancelled his scheduled meeting with President Donald J. Trump in Washington the following week, rejecting the visit after Trump ordered a border wall between the two nations.
President Trump Wall
Cost questioned
February 6, 2017: some Republican lawmakers expressed skepticism that the border wall was worth the price tag and asked that Trump offer off-sets for the cost.
Texas Senator, John Cornyn said: “I have concerns about spending un-offset money, which adds to the debt, period. I don’t think we’re just going to be able to solve border security with a physical barrier because people can come under, around it and through it.”
February 9, 2017: a leaked report from the Department of Homeland Security put the cost of building the wall (and fencing) at around three times as much as Trump originally estimated, $21 billion in total, and estimates that construction would take at least three years to complete. The report did not take into account “major physical barriers, like mountains, in areas where it would not be feasible to build.”
February 24, 2017: via the website FedBizOpps.gov the federal government posted their intention to request proposals from construction companies on March 6 to build the wall. The posting read:
The Dept. of Homeland Security, Customs and Border Protection (CBP) intends on issuing a solicitation in electronic format on or about March 6, 2017 for the design and build of several prototype wall structures in the vicinity of the United States border with Mexico. The procurement will be conducted in two phases, the first requiring vendors to submit a concept paper of their prototype(s) by March 10, 2017, which will result in the evaluation and down select of offerors by March 20, 2017. The second phase will require the down select of phase 1 offerors to submit proposals in response to the full RFP by March 24, 2017, which will include price. Multiple awards are contemplated by mid-April for this effort. An option for additional miles may be included in each contract award.
The deadline was eventually delayed until April 4.
President Trump Wall
A Great Wall…
February 28, 2016: In his first address to a joint session of Congress, President Trump declared:
We must restore integrity and the rule of law to our borders…For that reason, we will soon begin the construction of a great wall along our southern border. It will be started ahead of schedule and, when finished, it will be a very effective weapon against drugs and crime.
March 16, 2017: President Trump unveiled his budget blueprint for 2018, which included $2.6 billion for the wall. In the spending outline for the Department of Homeland Security it read:
The President’s 2018 Budget…Secures the borders of the United States by investing $2.6 billion in high-priority tactical infrastructure and border security technology, including funding to plan, design, and construct a physical wall along the southern border
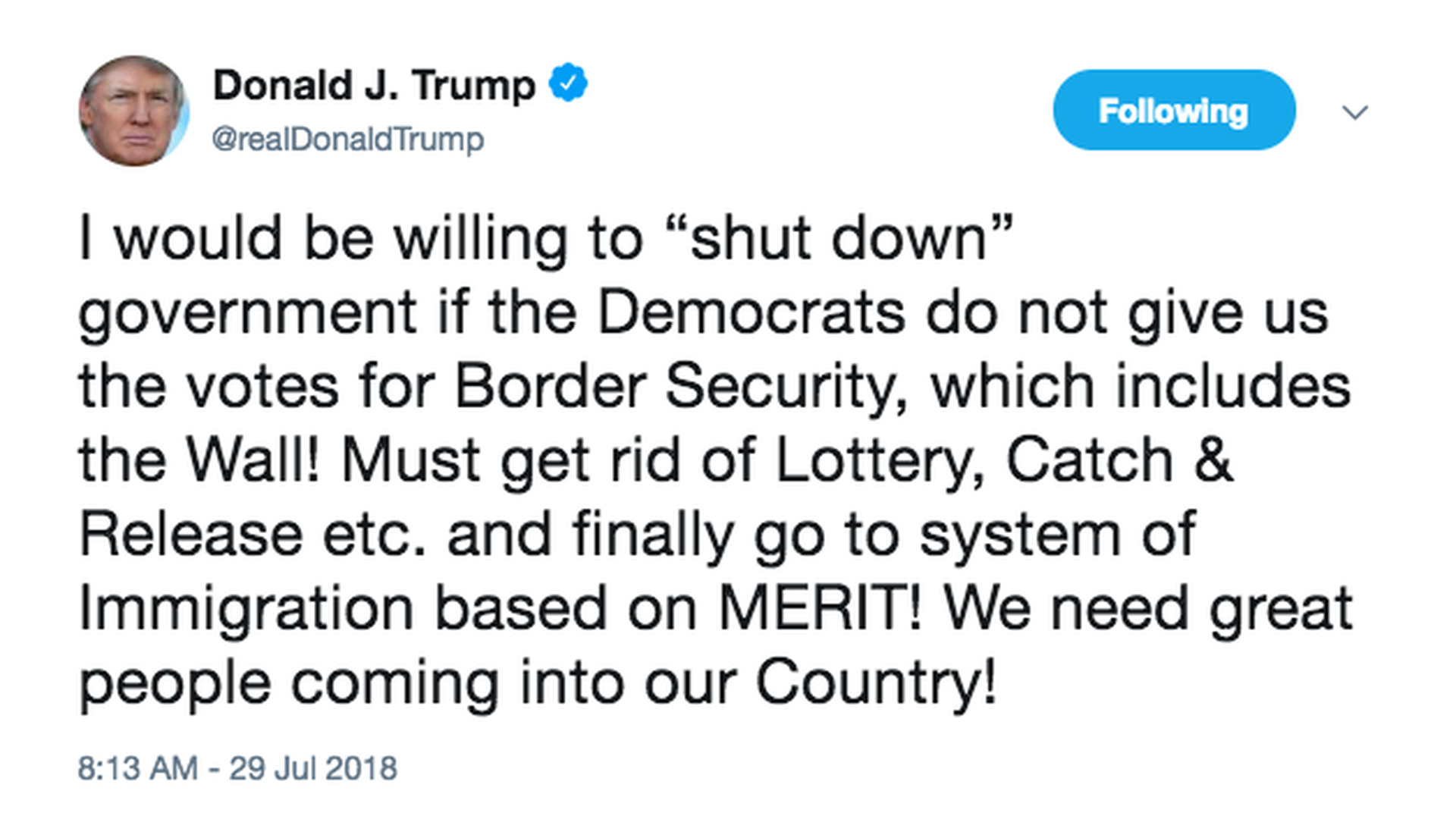
He also requests $1.5 billion to be added to spending for the current fiscal year. The administration began to that the funding for the wall be tied to the spending bills aimed at preventing government shutdown at the end of April.
President Trump Wall
A solar wall…
June 21, 2017: Trump told a crowd in Cedar Rapids, Iowa, “We’re thinking about building the wall as a solar wall so it creates energy and pays for itself and this way Mexico will have to pay much less money, and that’s good, right? Is that good?”
The solar wall idea was later abandoned.
President Trump Wall
A see-thru wall…
July 12, 2017: Trump added a new component to the wall: it had to be see-through. And, for the first time, he proposed a “steel wall with openings.”
“One of the things with the wall is you need transparency. You have to be able to see through it,” Trump told reporters on Air Force One. “So it could be a steel wall with openings, but you have to have openings because you have to see what’s on the other side of the wall.
“When they throw the large sacks of drugs over, and if you have people on the other side of the wall, you don’t see them – they hit you on the head with 60 pounds of stuff? It’s over.”
January 11, 2018: Trump explained to The Wall Street Journal that border officials told him “they need see-through” and indicated a concrete wall might be the wrong thing because of that.
“We need a form of fence or window,” Trump said.
“If you have a wall this thick and it’s solid concrete from ground to 32 feet high, which is a high wall, much higher than people planned. You go 32 feet up and you don’t know who’s over here,” he explained. “If you don’t know who’s there, you’ve got a problem.”
He also said the wall did not need to run the course of the entire border because of natural barriers. But he also insisted “the wall’s identical” to what he promised on the campaign trail.
January 18, 2018: Trump tweeted in response to a Washington Post report that White House Chief of Staff John Kelly had said “a concrete wall from sea to shining sea” was not going to happen and that Trump’s campaign promises about the wall were “uninformed.”
President Trump Wall
A perfecto wall…
March 13, 2018: President Trump reviewed eight prototypes for the wall in San Diego during a visit to the border.
All of the designs were concrete, but only one included the see-through component Trump said was necessary. He also repeated the need for a tall wall, comparing some migrants to “professional mountain climbers.”
“We want to make it perfecto,” he said of the wall.
Proud to shut down the government…
December 11, 2018: President Trump Meeting with Democratic Leaders. President Trump said he would be proud to “shut down the government for border security” in an Oval Office exchange with then House Minority Leader Nancy Pelosi (D-CA) and Senate Minority Leader Chuck Schumer (D-NY). The leaders went back and forth over border security, building the wall, and the congressional support and votes needed to pass funding legislation on this issue. [full transcript of meeting]
December 21, 2018: President Trump shared a design of a tall fence on Twitter, which he referred to as a “Steel Slat Barrier.”
“Totally effective while at the same time beautiful!” he said.
President Trump Wall
Partial shutdown commences
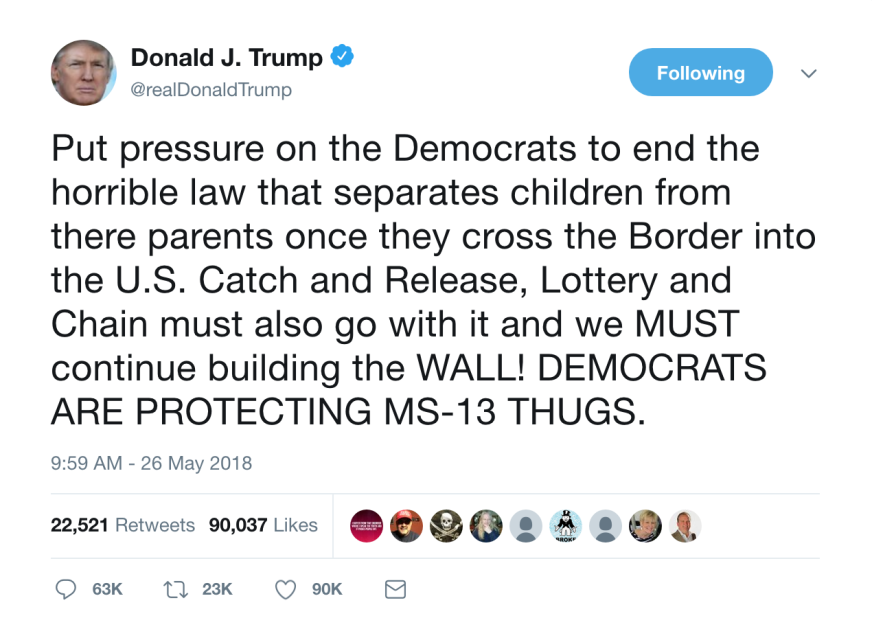
December 22, 2018: with Democratic leaders refusing to provide funds for President Trump’s wall project and President Trump refusing to negotiate to a budget compromise, a partial shutdown of the federal government began.
December 25, 2018: President Trump said, “”I can’t tell you when the government is going to reopen,” Trump told reporters in the Oval Office. “I can tell you it’s not going to be open until we have a wall, a fence, whatever they’d like to call it. I’ll call it whatever they want. But it’s all the same thing. It’s a barrier from people pouring into our country.”
December 31, 2018: “An all concrete Wall was NEVER ABANDONED, as has been reported by the media,” President Trump tweeted ahead of New Year’s Eve. “Some areas will be all concrete but the experts at Border Patrol prefer a Wall that is see through (thereby making it possible to see what is happening on both sides). Makes sense to me!”
The president was evidently reacting to a Los Angeles Times interview in which Kelly said, “To be honest, it’s not a wall.”
“The president still says ‘wall’ – oftentimes frankly he’ll say ‘barrier’ or ‘fencing,’ now he’s tended toward steel slats. But we left a solid concrete wall early on in the administration, when we asked people what they needed and where they needed it,” Kelly told the Times.
President Trump Wall
The Wall is coming
January 5, 2019: with Trump and the Democratic leadership remaining adamant in their positions on building a wall, in a tweet President Trump referenced the popular Game of Thrones slogan, Winter Is Coming, with “The Wall is Coming,” with a picture of himself over the wall.
January 6, 2019:President Trump tweeted, “”We are now planning a Steel Barrier rather than concrete. It is both stronger & less obtrusive. Good solution, and made in the U.S.A.”
January 8, 2019: President Trump made a national address on the escalating controversy over U.S.-Mexico border wall funding, which was continued to cause a partial federal government shutdown.
January 9, 2019: President Trump stormed out of a White House meeting with congressional leaders after Speaker Nancy Pelosi said she would not fund a border wall even if he agreed to reopen the government, escalating a confrontation that has shuttered large portions of the government for 19 days and counting.
Democrats emerged from the meeting in the White House Situation Room declaring that the president had thrown a “temper tantrum” and slammed his hands on the table before leaving with an abrupt “bye-bye.” Republicans disputed the hand slam and blamed Democratic intransigence for prolonging the standoff.
January 10, 2019: as the government shutdown neared the end of its third week and with no additional negotiations scheduled with congressional leaders, President Trump left Washington to visit the southern border.
In brief remarks to reporters Trump left open the possibility of declaring a state of emergency, which could allow him to bypass Congress to fund the wall.
President Trump Wall
Let’s Make a Deal
January 19, 2019: President Trump announced that he would extend deportation protections for some undocumented immigrants in exchange for $5.7 billion in funding for a wall along the border with Mexico.
The president said he would extend the legal status of those facing deportation and support bipartisan legislation that would allow some immigrants who came to the United States illegally as children, known as Dreamers, to keep their work permits and be protected from deportation for three more years if they were revoked.
Speaker Nancy Pelosi said ahead of his remarks that she considered his proposal a “nonstarter,” in part because it offered no permanent pathway to citizenship for Dreamers.
No Deal
January 25, 2019: Trump agreed to reopen the federal government for three weeks while negotiations continued over how to secure the nation’s southwestern border, backing down after a monthlong standoff failed to force Democrats to give him billions of dollars for his long-promised wall.
February 2019
New Mexico Troop withdrawal
February 5, 2019: Gov. Michelle Lujan Grisham of New Mexico ordered the withdrawal of the majority of the state’s National Guard troops from the U.S. border with Mexico, in a move that challenges President Trump’s description of a security crisis.
Grisham announced the partial withdrawal shortly before Trump’s State of the Union address. Her Republican predecessor deployed National Guard troops to the border in April 2018 at Trump’s suggestion, and 118 remained there before Tuesday’s reversal.
“New Mexico will not take part in the president’s charade of border fear-mongering by misusing our diligent National Guard troops,” Lujan Grisham said in a statement.
At the same time, the governor said a small contingent — around a dozen guardsmen — will remain in the southwestern corner of the state to assist with humanitarian needs in a remote corridor for cross-border immigration. She also mobilized state police to assist local law enforcement.
California Troop withdrawal
February 11, 2019: Gov. Gavin Newsom of California ordered the withdrawal of nearly 400 of his state’s National Guard troops from deployment along the border with Mexico and assigned them to other duties.
The step to rescind state authorization for the border deployment was a sharp rebuke of President Trump’s continued warnings that undocumented migrants present a national security risk to the United States.
Under a “general order,”110 California National Guard troops would be redirected to support the state’s central fire agency, Cal Fire, and another 100 will work on statewide “intelligence operations” aimed at international criminal drug gangs.
“National Emergency”
February 15, 2019: President Trump declared a national emergency on the border with Mexico in order to access billions of dollars that Congress refused to give him to build a wall there, transforming a highly charged policy dispute into a confrontation over the separation of powers outlined in the Constitution.
Trying to regain momentum after losing a grinding two-month battle with lawmakers over funding the wall, Mr. Trump asserted that the flow of drugs, criminals and illegal immigrants from Mexico constituted a profound threat to national security that justified unilateral action.
“We’re going to confront the national security crisis on our southern border, and we’re going to do it one way or the other,” he said in a televised statement in the Rose Garden barely 13 hours after Congress passed a spending measure without the money he had sought. “It’s an invasion,” he added. “We have an invasion of drugs and criminals coming into our country.”
Emergency challenged
February 18, 2019: a coalition of 16 states challenged President Trump in court over his plan to use emergency powers to spend billions of dollars on his border wall.
The suit, filed in Federal District Court in San Francisco, argued that the president did not have the power to divert funds for constructing a wall along the Mexican border because it was Congress that controls spending. [Read the full lawsuit here.]
House votes to overturn emergency
February 26, 2019: the House voted to overturn President Trump’s declaration of a national emergency on the Mexican border, with just 13 Republicans joining Democrats to try to block his effort to divert funding to a border wall without congressional approval.
House Republican leaders kept defections low after feverishly working to assuage concerns among rank-and-file members about protecting congressional powers and about the precedent that Trump could be setting for Democratic presidents to use for their own purposes.
March 2019
“Shoot them in the legs”
In March 2019: at an Oval Office meeting, President Trump ordered advisors to shut down the entire 2,000-mile border with Mexico — by noon the next day.
The advisers feared the president’s edict would trap American tourists in Mexico, strand children at schools on both sides of the border and create an economic meltdown in two countries.
Privately, the president had often talked about fortifying a border wall with a water-filled trench, stocked with snakes or alligators, prompting aides to seek a cost estimate. He wanted the wall electrified, with spikes on top that could pierce human flesh. After publicly suggesting that soldiers shoot migrants if they threw rocks, the president backed off when his staff told him that was illegal. But later in a meeting, aides recalled, he suggested that they shoot migrants in the legs to slow them down. That’s not allowed either, they told him. [NYT article]
Money for the Wall
March 10, 2019: President Trump requested $8.6 billion in the annual budget proposal for a border wall. He also asked Congress for another $3.6 billion to replenish military construction funds he had diverted to begin work on the wall by declaring a national emergency, for a total of $12.2 billion.
Senate votes to overturn emergency
March 14, 2019: the Senate easily voted to overturn President Trump’s declaration of a national emergency at the southwestern border, delivering a bipartisan rebuke to what lawmakers in both parties deemed executive overreach by a president determined to build his border wall over Congress’s objections.
The 59-41 vote on the House-passed measure set up the first veto of Trump’s presidency. It was not overwhelming enough to override Mr. Trump’s promised veto, but Congress has now voted to block a presidential emergency declaration for the first time — and on one of the core promises that animated Mr. Trump’s political rise, the vow to build a wall between the United States and Mexico.
“Never before has a president asked for funding, Congress has not provided it, and the president then has used the National Emergencies Act of 1976 to spend the money anyway,” Senator Lamar Alexander, Republican of Tennessee, said. “The problem with this is that after a Revolutionary War against a king, our nation’s founders gave to Congress the power to approve all spending so that the president would not have too much power. This check on the executive is a crucial source of our freedom.”
Veto
March 15, 2019: as he had said he would, President Trump vetoed the bill denying his declaration of a national emergency.
No override
March 26, 2019: the House failed to overturn President Trump’s veto, leaving the declaration of a national emergency at the southwestern border intact despite the bipartisan passage of a resolution attempting to nullify the president’s circumvention of Congress to fund his border wall.
The 248-to-181 vote fell short of the two-thirds majority needed to kill the national emergency declaration.
Litigation stops funds
US District Court
May 24, 2019: Judge Haywood Gilliam of the United States District Court for the Northern District of California granted a preliminary injunction that prevented the Trump administration from redirecting funds under the national emergency declaration issued on February 15.
Gilliam, who is overseeing a pair of lawsuits over border wall financing, ruled that the administration’s efforts likely overstepped the president’s statutory authority.
The injunction applied specifically to some of the money the administration intended to allocate from other agencies, and it limited wall construction projects in El Paso, Tex., and Yuma, Ariz.
The ruling quoted from a Fox News interview with Mick Mulvaney, the acting White House chief of staff, in which he said that the wall “is going to get built, with or without Congress.”
US Appeals Court
July 3, 2019: the Ninth Circuit federal appeals court in San Francisco upheld a block on President Trump’s attempt to use $2.5 billion from the Department of Defense to construct a wall along the southwestern border.
The divided three-judge panel agreed with a lower court’s decision that ruled the Trump administration did not have the authority to reallocate the funds without congressional approval. The administration immediately appealed.
Two of the three judges on the panel affirmed that the administration could not build the barriers during future challenges.
“We conclude that it is best served by respecting the Constitution’s assignment of the power of the purse to Congress, and by deferring to Congress’s understanding of the public interest as reflected in its repeated denial of more funding for border barrier construction.”
Supreme Court
July 26, 2019: the Supreme Court gave President Trump a victory in his fight for a wall along the Mexican border by allowing the administration to begin using $2.5 billion in Pentagon money for the construction.
In a 5-to-4 ruling, the court overturned an appellate decision and said that the administration could tap the money while litigation over the matter proceeds. But that will most likely take many months or longer, allowing Mr. Trump to move ahead before the case returns to the Supreme Court after further proceedings in the appeals court.
Second Veto
October 15, 2019: President Trump issued his second veto against legislation seeking to end his national emergency at the southwestern border, rejecting bipartisan objections to his efforts to obtain funds for a border wall.
His veto returned the resolution to Congress where it was unlikely to garner the two-thirds majority needed there to override the veto.
The announcement came exactly seven months after Trump had issued the first veto of his presidency against a nearly identical resolution that would have terminated the national emergency. He declared the emergency earlier this year after Congress declined to designate money for his border wall; he has sought to allocated funds from other government agencies to the southwestern border.
Trump, announcing the veto, noted that he had vetoed the earlier measure “because it was a dangerous resolution that would undermine United States sovereignty and threaten the lives and safety of countless Americans.” [NYT article]
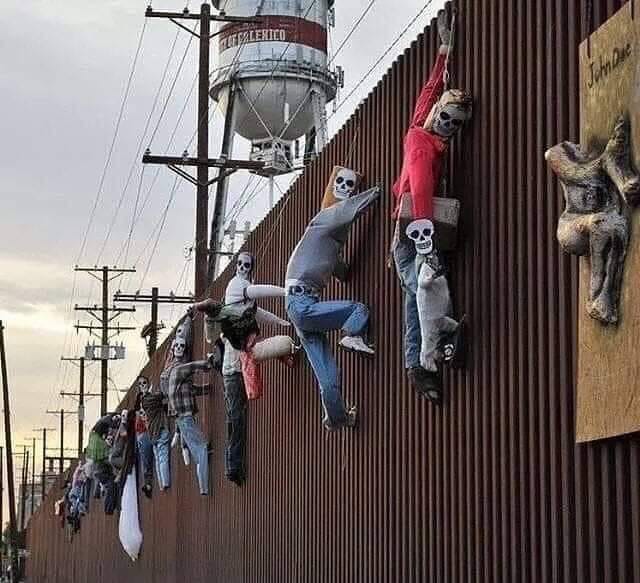

Cutting through the wall
November 2, 2019: according to the Washington Post, smugglers were using a commercial saw to cut through newly built sections of the president’s wall— which is made of steel bollards that are partially filled with concrete.
The tool can cut through the wall’s steel and concrete in minutes when fitted with the appropriate blades, Customs and Border Protection (CBP) agents have said. After cutting the steel bollards, smugglers have taken to returning them to their original positions in hope of reusing the passage without being detected by border officials.
Agents mended the breach, however, repaired sections are still targeted by smugglers, as it was easier to cut through the welded metal than to make new cuts. And the repair policy had also been targeted by smugglers who attempt to fool agents into believing a severed bollard has been fixed by applying putty to the site of the cut. [VOX story]
Funding Wall limited
December 10, 2019: Judge David Briones of the US District Court for the Western District of Texas said that the administration cannot use military construction funds to build additional barriers on the southern border.
The ruling was a setback for the administration, which has sought to shore up money for the President’s signature campaign promise of a border wall, and marks yet another high-profile blow the courts have dealt Trump on key issues, including his immigration policies and his fight to not turn his tax returns over to Congress. It targeted only one set of Pentagon funds, however, leaving in place the money the Supreme Court allowed to be used earlier this year. [CNN article]
President Trump Wall
2020
Court allows Wall funding
January 8, 2020: in a 2-1 ruling, the 5th Circuit Court of Appeals allowed the Trump administration to use a certain set of Defense Department funds for the construction of the border wall after a lower court blocked the administration from dipping into them on December 10.
The ruling marked a victory for President Donald Trump, who had sought to shore up funds for his signature border wall. The money was separate from other funds that the Supreme Court allowed to be used last year on July 26, 2019. The case was still ongoing.
Wall’s cost
January 19 2020: based on a status report that U.S. Customs and Border Protection, which is overseeing wall construction, had released, on this date, NPR reported that the pricetag for President Trump’s border wall had topped $11 billion — or nearly $20 million a mile — and would become the most expensive wall of its kind anywhere in the world. $11 billion had been identified since Trump took office to construct 576 miles of a new “border wall system.”
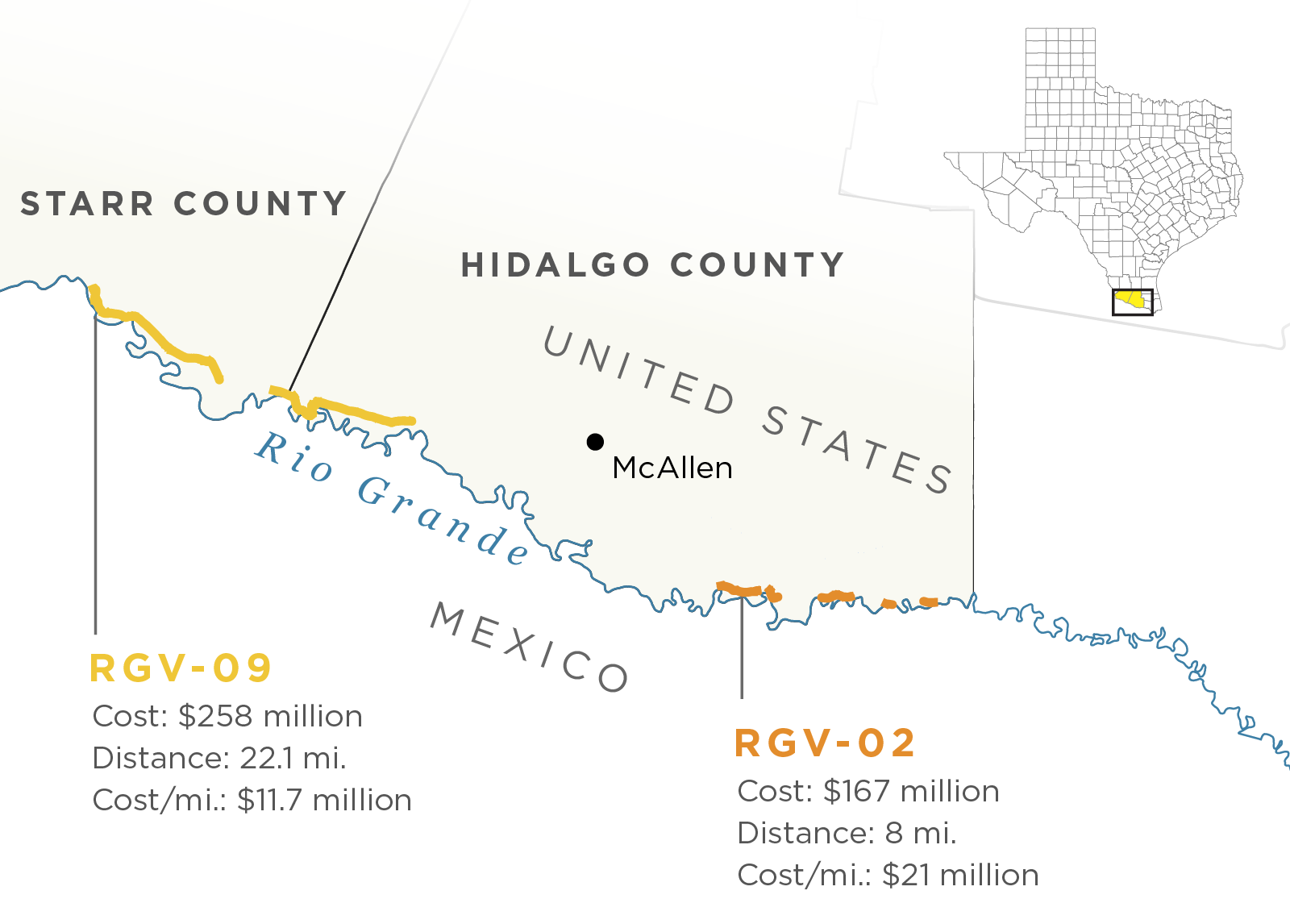
Native American burial site desecrated
February 7, 2020: CBS News reported that US border contractors had begun “controlled blasting” at a sacred burial grounds where members of the Tohono O’odham Nation buried their ancestors to make way for President Donald Trump’s US-Mexico border wall
The site is located inside Arizona’s Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument on land adjacent to the Tohono O’odham Nation. Archaeologists touring the site before construction said they found human remains dating back 10,000 years.
“The construction contractor has begun controlled blasting, in preparation for new border wall system construction, within the Roosevelt Reservation at Monument Mountain in the US Border Patrol’s Tucson Sector,” the US Customs and Border Protection said in a statement.
President Trump Wall
Trump Boasts About His Wall
June 23, 2020: the NY Times reported that President Trump traveled to Yuma, Arizona with a renewed anti-immigrant appeal, bragging about the progress his administration has made in constructing a “big, beautiful wall.”
“My administration has done more than any administration in history to secure our southern border,” Mr. Trump boasted, citing the completion of about 220 miles of what he called a “powerful new” wall on the border. “It’s the most powerful and comprehensive border wall structure anywhere in the world.”
Border and immigration officials lauded his “leadership and determination” and repeatedly thanked the president for what Mark Morgan, the acting commissioner of Customs and Border Protection, called “220 new miles of wall system that gives us an enhanced capability that we never had.”
In fact, all but three of the 216 miles of border wall constructed by the Trump administration are essentially much larger replacements of existing, dilapidated fences or vehicle barriers — a fact that Mr. Trump and his immigration advisers routinely dismiss.
President Trump Wall
Judicial Setback
October 9, 2020: the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals ruled that President Trump’s use of emergency powers to allocate millions of dollars in funding for the construction of a southern border wall was illegal, the latest blow to the Trump administration’s effort to limit immigration.
In the 2-1 decision, the court upheld a December 2019 district court summary judgment in favor of a request from the advocacy groups the Sierra Club and the Southern Border Communities Coalition against Defense Secretary Mark Esper, acting Homeland Security Secretary Chad Wolf and “all persons acting under their direction … from using military construction funds appropriated for other purposes to build a border wall.” [The Hill article]
President Trump Wall
Last stand
January 12, 2021: a week before the end of his term, President Trump traveled to Alamo, Texas, near the border, to mark the completion of more than 450 miles of the border wall.
The wall, which Trump repeatedly cited over the last four years as an accomplishment, cost US taxpayers — not Mexico — billions and became emblematic of the President’s restrictionist immigration policies, which largely sealed the US off from immigrants and refugees.
During a brief speech near the wall, Trump listed off a series of those policies, citing them as accomplishments and calling them “historic.”
Many of the policies rolled out over the last four years were unprecedented, including requiring asylum seekers to wait in Mexico until their immigration court date in the US and swiftly removing migrants arriving at the southern border under a public health order. Immigrant advocates and lawyers had challenged the policies in court, arguing that they put migrants in harm’s way. [CNN article]
President Trump Wall
Trump Exits; Biden Enters
January 20, 2021: President Biden halted construction of President Trump’s border wall with Mexico. The order included an “immediate termination” of the national emergency declaration that had allowed the Trump administration to redirect billions of dollars to the wall. It said the administration would begin “a close review” of the legality of the effort to divert federal money to fund the wall. [NYT article]